low end tidal co2 after intubation
An end-tidal carbon dioxide level of 10 mmHg or less measured 20 minutes after the initiation of advanced cardiac life support accurately predicts death in patients with cardiac arrest associated with electrical activity but no pulse. Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project 3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status.

. Breath sounds were distant after the second intubation. Age gender vital signs laboratory findings are recorded. A high peak of the alveolar phase in poorly compliant lungs.
The mean age of the 48 patients was 74 years. Alveolar dead space may be increased in most types of lung disease reflecting dysfunction at the alveolar vascular or airway level. Immediately after intubation as measured by the capnography the initial PETCO2_1 and at post-ventilation 15 min PETCO2_2 and first second arterial blood gas analysis are recorded.
Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO. Consequently a strategy of high-frequency low-tidal volume breaths will tend to achieve less CO2 clearance for any specific total minute ventilation.
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. The effectiveness of out-of-hospital use of continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring on the rate of unrecognized misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services system.
Over the ensuing minute the patients oxygen saturation declined from 93 to 82 and the end-tidal carbon dioxide decreased to 10 mm Hg. A low end-tidal CO2 in hypothermia. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as.
The PETCO2_1 and PETCO2_2 measurements were. A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in children with DKA. The normal values of end-tidal CO 2 is around 5 or 35-37 mm Hg.
Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2. 2345 ETCO 2 monitoring is one of the objective standards set in the Intensive. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.
Ad View a brochure to learn about end-tidal CO2 capnography. End-tidal carbon dioxide reflects CO 2 concentration of alveoli emptying last. Congratulations youre in the oesophagus.
Multiple monitoring options so you can choose what and how to monitor respiratory status. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Reassess tube placement patency and depth in.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Bhende MS Karasic DG Karasic RB. A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation.
The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg.
Though initially there is some CO 2 returning though the tube one finds with subsequent breaths the end tidal graph is lower and lower and the patient is getting more and more hypoxic. End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in. For example increased dead space is seen in pulmonary embolism in pneumonia or.
During this period approximately 10 carbon dioxide square waves were observed. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. The Difference Between Arterial and End Tidal CO2.
After intubation if ETCO 2. End-tidal CO2 measurement in the detection of esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest.

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Ventilator Waveform Troubleshooting High Peak Pressures This

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Capno 101 How Does Capnography Work Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Tutor By Satish Deopujari Tutor Telemedicine Learning

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy
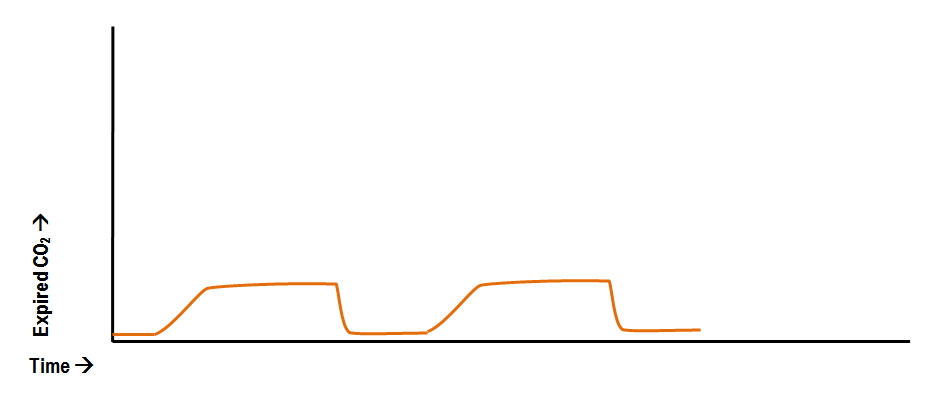
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

